Blockchain architecture explained
Blockchain technology has already disrupted various industries. Many companies are looking for innovative solutions that can be built on a blockchain architecture.
As companies race to adopt blockchain technology, many find the need for blockchain architecture experts.
How does blockchain work, what problems does it solve, and how can it be used? In this article, we will discuss what blockchain architecture is and how it can be used to build software development solutions.
What is blockchain technology?
Let’s first explain blockchain technology. A blockchain is a distributed and public digital book (ledger) database that uses cryptography to provide any information.
To illustrate what blockchain technology is, imagine the following scenario. You go for your weekly shopping, fill the cart and come to the cash register. You are waiting in line. After a few minutes, you find out that your card is not working. Your bank’s system has crashed, and you can’t pay anything.
But imagine a world where the cash register has access to the general ledger of finances, in which the balance on your credit or debit card is visible, and it is updated every time you buy something?
Even if the bank system crashes, your card still works because the cashier knows the actual balance of your account. Great, isn’t it?
This is just one of the benefits of the so-called distributed (decentralised) ledger of transactions, better known as a blockchain.
Blockchain gets rid of the intermediary. Since the beginning of the bank system, many years ago, we traded our ability to have control for convenience and put trust in a third party.
For example, you want to transfer some money to a friend. You want to pay with a credit card and just swipe it. You have convenience, but you pay for that with fees and your trust. The money you want to transfer goes through an intermediary.
Here we have things in a centralized database which is an app for money transfers. The app is hosting data and protecting it and we trust them to keep it secure. Blockchain has solved this “middleman” problem by creating a series of networks of nodes to be able to distribute the responsibility across the entire network.
In this case, we trust the software to do it for us and distribute it across the network, which is highly secure. In this case, we trust the code.
The person sending money and the person receiving money both have a copy of the ledger, and the middleman is gone. This is a “trustless” ecosystem because they don’t even have to know each other or trust each other; the system does it for them.
What is blockchain architecture?
Here is blockchain architecture simplified and explained:
Blockchain architecture is a term used in software development to describe blockchain technology in designing and developing software solutions.
The use of blockchain technology in software development helps create more secure and transparent systems. It is widely used in the financial industry to help develop software development solutions for cryptocurrencies, record keeping, smart contracts, and digital notaries.
A blockchain is virtually impossible to hack because there is no centralized information in its architecture.
Blockchain architecture is the structural design of a blockchain system. It determines how the blockchain will function and how transactions will be processed.
There are three main components of blockchain architecture:
- Network: made up of computers that participate in the blockchain system.
- Protocol: a set of rules that governs how the network communicates and how transactions are processed.
- Ledger: a tamper-proof record of all transactions on the blockchain.
Blockchain architecture ensures that all these components work together harmoniously to create a secure and efficient blockchain system.
What are some best practices for using blockchain architecture?
The use of blockchain technology in software development helps create more secure and transparent systems, which is why it is widely used in the financial industry to develop solutions for cryptocurrencies, record keeping, smart contracts, and digital notaries.
There are a few best practices to keep in mind when it comes to blockchain architecture.
Smart contracts
Another key element of blockchain architecture is the use of smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts stored on the blockchain and can be used to automate transactions. For example, you could use a smart contract in a supply chain industry to pay a supplier once goods have been delivered automatically.
KYC and AML
KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) are two widely accepted practices that can benefit from blockchain technology. Currently, financial institutions must complete an extensive multi-step KYC and AML process for each client, which is costly. In this process, blockchain could reduce costs by performing a KYC/AML check on a given client and making the results available to all financial institutions while also increasing the efficiency of analysis and monitoring.
Medical documentation
Blockchain technology has the potential to standardize the secure electronic exchange of medical records between healthcare providers. It enables a decentralized records management system, removing the need for an organization to manage patient access to records. Potential benefits of blockchain-enabled healthcare applications include instantly verifying the authenticity of prescriptions and automatically detecting the possibility of harmful drug interactions.
Key components of blockchain architecture
Here is a list of the architectural components of blockchain:
Transaction
Transactions are data structures that encode the transfer of value between participants in the blockchain system. They typically include a recipient address, a sender address, and a value. The value is transferred by the owner digitally signing the hash created by adding the previous transaction and the receiver’s public key.
Blocks
Blocks are data structures that are replicated to all nodes in the network and are used to bundle sets of transactions. Block contains information in the form of a block header and transactions. Miners create blocks in the blockchain.
Mining is the process of creating a valid block that the rest of the network will accept. Nodes accept pending transactions, validate them cryptographically, and package them into blocks to be stored on the blockchain. The blocks bind to each other, and this makes the blockchain impenetrable. Once a block is locked, the flow and time of transactions are known.
P2P Network
P2P networks are supported by a decentralized ledger of transactions and are a key component of blockchain technology.
The primary goal that drove the creation of Bitcoin, the most widely used cryptocurrency, was a strictly peer-to-peer exchange of currency.
Peer-to-peer refers to the direct exchange of some asset, such as digital currency, between individual parties without the involvement of a central authority. It is a group of devices linked together to form a peer-to-peer network (P2P) network.
Once established, the network can be used to share and store files. All nodes have equal power in any peer-to-peer network and can perform the same tasks.
The definition of a peer-to-peer network varies depending on the industry. For example, a P2P network in the financial sector or technology can be a distributed network where peers can exchange digital assets or cryptocurrencies. This allows sellers and buyers (peers) to buy and sell without intermediaries.
Consensus Algorithm
The consensus algorithm is the process by which all nodes/validators in a blockchain network reach a joint agreement on the current state of a distributed ledger.
The consensus protocol ensures that every new block added to the blockchain is the only version of the truth that all the nodes in the blockchain agree on. In this way, consensus algorithms achieve transparency in the blockchain network and establish trust between unknown participants in a distributed computing environment.
One could argue that the consensus algorithm is at the heart of every blockchain architecture. Here are some of the consensus algorithms:
Proof-of-Work (POW): done by miners who compete to create new blocks full of processed transactions.
Proof-of-Stake (POS): done by validators who have staked ETH to participate in the system.
Main characteristics of the blockchain architecture
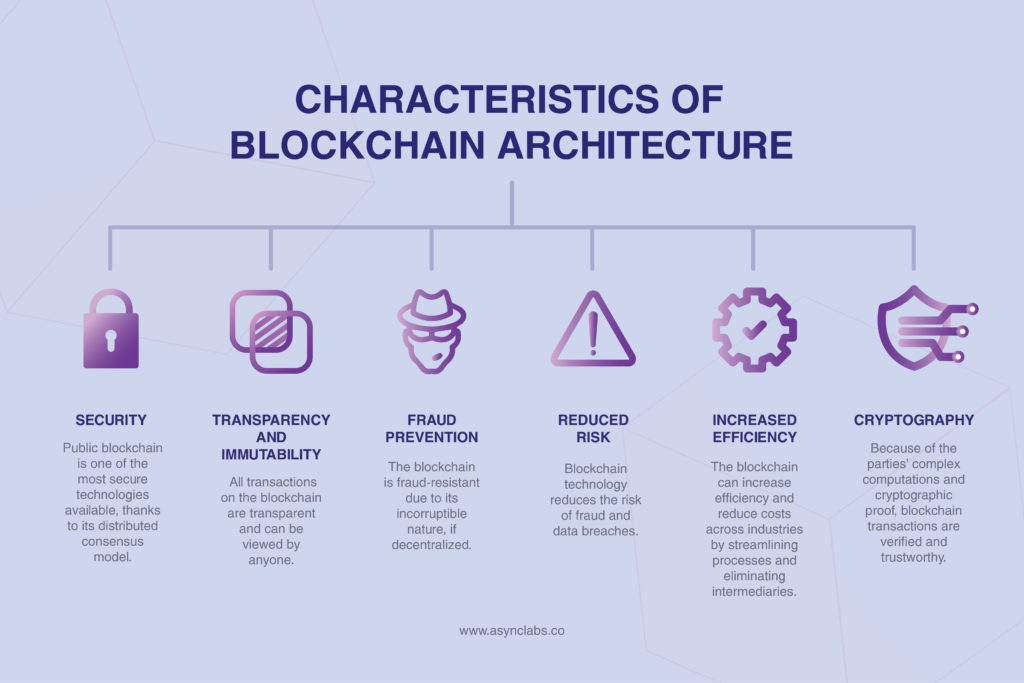
What sets blockchain apart?
Blockchain is a game-changer for many industries as an immutable and transparent digital ledger. So, what makes blockchain so unique? Here are six key advantages and disadvantages of blockchain architecture:
- Security: Public blockchain is one of the most secure technologies available, thanks to its distributed consensus model.
But, if we speak about private blockchain, one entity has control over the addition of new blocks, i.e., it can add and delete transactions.
- Transparency and immutability: All transactions on the blockchain are transparent and can be viewed by anyone.
It can be transparent and immutable. It all depends on consensus (Proof of Authority, for example) and how centralized it is. The more centralized, the less transparent it is.
- Fraud prevention: The blockchain is fraud-resistant due to its incorruptible nature if decentralized.
The more centralized it is, the more the primary entity can influence transactions – rug pulling or committing fraud, which is a big minus.
- Reduced risk: Blockchain technology reduces the risk of fraud and data breaches.
- Increased efficiency: The blockchain can increase efficiency and reduce costs across industries by streamlining processes and eliminating intermediaries.
When speaking of public blockchains, they can be slow due to network congestion, which means that transactions do not pass or are very expensive. This is a big drawback. On the other hand, private blockchains are fast, but they are not entirely immutable since one entity has a large portion of control over the network.
- Cryptography — Because of the parties’ complex computations and cryptographic proof, blockchain transactions are verified and trustworthy.
The security of blockchain
Security is one of the key benefits of blockchain technology. How?
By design, blockchains are secure. This is because a blockchain is essentially a transparent and tamper-proof ledger of all transactions that have ever taken place on it. Once data is entered into a blockchain, it is difficult to change or remove.
For this reason, blockchains are perfect for storing sensitive data and creating trust between multiple parties. For example, imagine if you were buying a house. You would want to know that the sale records were secure and could not be tampered with. A blockchain could provide that security.
The decentralization of blockchain
One of the key features that make blockchain so unique is its decentralization. This means that there is no central authority controlling the network. Instead, it’s maintained by a group of users known as “nodes.” This ensures that the network is incredibly secure and difficult to hack.
It also means that there’s no need for a third party to validate transactions, as the nodes do this. This speeds up the process and reduces costs, as there’s no need for expensive intermediaries.
The transparency of blockchain
One of the key characteristics that set blockchain apart is its transparency. Blockchain is a distributed database that allows anyone in the network to view all of the processed transactions. This level of transparency creates a level of trust that is unparalleled in other technologies.
Furthermore, because blockchain is decentralized, there is no one central authority that can control or modify the data. This ensures that the data is truthful and tamper-proof.
The efficiency of blockchain
One of the most remarkable features of blockchain is its efficiency. Transactions are verified and completed almost instantly, eliminating the need for third-party involvement. This also cuts down on waiting times and keeps costs low.
Not only is blockchain efficient, but it’s also secure. The cryptographic security of blockchain makes it virtually impossible to hack, making it a more reliable option for businesses looking to store sensitive data.
Last but not least, blockchain is transparent. All transactions on the blockchain are recorded and can be viewed by anyone. This creates a high level of trust and accountability.
The immutability of blockchain
One of blockchain technology’s most unique and valuable features is its immutability. Once data has been written to a blockchain, it is challenging to change or delete. This makes the blockchain a reliable and trustworthy source of information, as it is practically impossible to tamper with.
This immutability also ensures that data cannot be manipulated, which is critical for industries such as finance and healthcare that require secure and reliable information storage. It also helps prevent fraud and boost transparency among businesses and consumers.
How to start building blockchain architecture?
In terms of the programming skills needed to develop a blockchain solution, there are some programming languages developers need to be familiar with.
Programming languages such as C++, Python, C, Java, and Ruby can be used to create a custom blockchain system, as well as web development skills such as HTML, CSS, and Node.js knowledge.
If you want to write smart contracts in Ethereum, you’ll need to be familiar with Solidity. Blockchain developers must understand business requirements and operations, have excellent collaboration and negotiation skills, and have complex programming skills.
Conclusion
Blockchain architecture has many opportunities for companies and developers to use it to build innovative software development solutions. Before starting any project, it is important to understand the basics of blockchain architecture.
By understanding how to use blockchain architecture and how to build blockchain architecture, companies can enjoy a wide range of benefits, from increased security and efficiency to reduced costs and improved transparency. While there are some challenges to overcome, the potential benefits of blockchain architecture make it well worth the effort.
As you can see, the blockchain architecture is quite complex but also has a lot of potential benefits for businesses. Some of the key benefits of blockchain technology include security, transparency, efficiency, and cost savings. As more and more businesses adopt blockchain technology, the future looks bright.
If you’re interested in implementing a blockchain project, be sure to get in touch with our team of experts. We can help you find the best solution for your specific needs and get your project up and running in no time.